ROC vs Precision-Recall Curves with N-Folds Cross-Validation
Using n-folds Cross Validation is a stapled piece to any problems for the sake of training. In this post, I have presented the ROC curves and Precision-Recall curves with n-folds Cross-Validation using XGBoost. The ROC one comes from Scikit-Learn documentation and I have customized it for Precision-Recall accordingly.
Loading Libraries
# Loading libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from scipy import interp
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, classification_report, accuracy_score, roc_curve, confusion_matrix, average_precision_score, precision_recall_curve
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, KFold, StratifiedKFold, train_test_split
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
import itertools
import glmnet
import xgboost as xgb
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_style("ticks")
mpl.rcParams['axes.linewidth'] = 3
mpl.rcParams['lines.linewidth'] = 2
from IPython.core.display import display, HTML
display(HTML("<style>.container { width:95% !important; }</style>"))
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
%matplotlib inline
Functions
def _plot_pr_nfolds_xgboost(df_X, Y,
n_folds = 10,
n_estimators = 100,
learning_rate = 0.05,
max_depth = 3,
min_child_weight = 5.0,
gamma = 0.5,
reg_alpha = 0.0,
reg_lambda = 1.0,
subsample = 0.9,
objective = "binary:logistic",
scale_pos_weight = 1.0,
shuffle = True,
random_state = 1367,
saveFigPath = None
):
"""
a function to plot k-fold cv Precision-Recall (PR) using xgboost
input parameters:
df_X : features : pandas dataframe (numpy array will be built inside the function)
Y : targets
n_folds : number of cv folds (default = 10)
n_estimators = number of trees (default = 100)
learning_rate : step size of xgboost (default = 0.05)
max_depth : maximum tree depth for xgboost (default = 3)
min_child_weight : (default = 5.0)
gamma : (default = 0.5)
reg_alpha : lasso penalty (L1) (default = 0.0)
reg_lambda : ridge penalty (L2) (default = 1.0)
subsample : subsample fraction (default = 0.9)
objective : objective function for ML (default = "binary:logistic" for classification)
scale_pos_weight : (default = 1.0)
shuffle : shuffle flag for cv (default = True)
random_state : (default = 1367
saveFigPath: name of the file for saving the figure as PDF format. (default = None))
"""
import numpy as np
from scipy import interp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc, precision_recall_curve
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams['axes.linewidth'] = 3
mpl.rcParams['lines.linewidth'] =7
# Defining the data + scaling
if isinstance(df_X, pd.DataFrame):
X = scale(df_X.values)
else:
X = scale(df_X)
y = Y
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
# #############################################################################
# Classification and PR analysis
# Run classifier with cross-validation and plot PR curves
cv = StratifiedKFold(n_splits = n_folds , shuffle = shuffle , random_state = random_state)
classifier = XGBClassifier(learning_rate = learning_rate,
n_estimators = n_estimators,
max_depth = max_depth,
min_child_weight = min_child_weight,
gamma = gamma,
reg_alpha = reg_alpha,
reg_lambda = reg_lambda,
subsample = subsample,
objective = objective,
nthread = 4,
scale_pos_weight = 1.,
base_score = np.mean(y),
seed = random_state,
random_state = random_state)
# defining the lists
prs = []
aucs = []
mean_recall = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
plt.figure(figsize=(18 , 13))
i = 0
for train, test in cv.split(X, y):
probas_ = classifier.fit(X[train], y[train]).predict_proba(X[test])
# Compute PR curve and area the curve
precision, recall, thresholds = precision_recall_curve(y[test], probas_[:, 1])
prs.append(interp(mean_recall, precision, recall))
pr_auc = auc(recall, precision)
aucs.append(pr_auc)
plt.plot(recall, precision, lw=3, alpha=0.5, label='Fold %d (AUCPR = %0.2f)' % (i+1, pr_auc))
i += 1
plt.plot([0, 1], [1, 0], linestyle='--', lw=3, color='k', label='Luck', alpha=.8)
mean_precision = np.mean(prs, axis=0)
mean_auc = auc(mean_recall, mean_precision)
std_auc = np.std(aucs)
plt.plot(mean_precision, mean_recall, color='navy',
label=r'Mean (AUCPR = %0.3f $\pm$ %0.2f)' % (mean_auc, std_auc),
lw=4)
plt.xlim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('Recall' , fontweight = "bold" , fontsize=30)
plt.ylabel('Precision',fontweight = "bold" , fontsize=30)
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=20)
plt.legend( prop={'size':20} , loc = 0)
if saveFigPath:
plt.savefig(F"./{saveFigPath}.pdf" ,bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def _plot_roc_nfolds_xgboost(df_X, Y,
n_folds = 10,
n_estimators = 100,
learning_rate = 0.05,
max_depth = 3,
min_child_weight = 5.0,
gamma = 0.5,
reg_alpha = 0.0,
reg_lambda = 1.0,
subsample = 0.9,
objective = "binary:logistic",
scale_pos_weight = 1.0,
shuffle = True,
random_state = 1367,
saveFigPath = None
):
"""
a function to plot k-fold cv ROC using xgboost
input parameters:
df_X : features : pandas dataframe (numpy array will be built inside the function)
Y : targets
n_folds : number of cv folds (default = 10)
n_estimators = number of trees (default = 100)
learning_rate : step size of xgboost (default = 0.05)
max_depth : maximum tree depth for xgboost (default = 3)
min_child_weight : (default = 5.0)
gamma : (default = 0.5)
reg_alpha : lasso penalty (L1) (default = 0.0)
reg_lambda : ridge penalty (L2) (default = 1.0)
subsample : subsample fraction (default = 0.9)
objective : objective function for ML (default = "binary:logistic" for classification)
scale_pos_weight : (default = 1.0)
shuffle : shuffle flag for cv (default = True)
random_state : (default = 1367
saveFigPath: name of the file for saving the figure as PDF format. (default = None))
"""
import numpy as np
from scipy import interp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams['axes.linewidth'] = 3
mpl.rcParams['lines.linewidth'] =7
# Defining the data + scaling
if isinstance(df_X, pd.DataFrame):
X = scale(df_X.values)
else:
X = scale(df_X)
y = Y
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
# #############################################################################
# Classification and ROC analysis
# Run classifier with cross-validation and plot ROC curves
cv = StratifiedKFold(n_splits = n_folds , shuffle = shuffle , random_state = random_state)
classifier = XGBClassifier(learning_rate = learning_rate,
n_estimators = n_estimators,
max_depth = max_depth,
min_child_weight = min_child_weight,
gamma = gamma,
reg_alpha = reg_alpha,
reg_lambda = reg_lambda,
subsample = subsample,
objective = objective,
nthread = 4,
scale_pos_weight = 1.,
base_score = np.mean(y),
seed = random_state,
random_state = random_state)
tprs = []
aucs = []
mean_fpr = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
plt.figure(figsize=(18 , 13))
i = 0
for train, test in cv.split(X, y):
probas_ = classifier.fit(X[train], y[train]).predict_proba(X[test])
# Compute ROC curve and area the curve
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y[test], probas_[:, 1])
tprs.append(interp(mean_fpr, fpr, tpr))
tprs[-1][0] = 0.0
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
aucs.append(roc_auc)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, lw=3, alpha=0.5,
label='ROC Fold %d (AUC = %0.2f)' % (i+1, roc_auc))
i += 1
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], linestyle='--', lw=3, color='k',
label='Luck', alpha=.8)
mean_tpr = np.mean(tprs, axis=0)
mean_tpr[-1] = 1.0
mean_auc = auc(mean_fpr, mean_tpr)
std_auc = np.std(aucs)
plt.plot(mean_fpr, mean_tpr, color='navy',
label=r'Mean ROC (AUC = %0.3f $\pm$ %0.2f)' % (mean_auc, std_auc),
lw=4)
std_tpr = np.std(tprs, axis=0)
tprs_upper = np.minimum(mean_tpr + std_tpr, 1)
tprs_lower = np.maximum(mean_tpr - std_tpr, 0)
plt.fill_between(mean_fpr, tprs_lower, tprs_upper, color='grey', alpha=.4,
label=r'$\pm$ 1 Standard Deviation')
plt.xlim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate' , fontweight = "bold" , fontsize=30)
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate',fontweight = "bold" , fontsize=30)
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=20)
plt.legend( prop={'size':20} , loc = 4)
if saveFigPath:
plt.savefig(F"./{saveFigPath}.pdf" ,bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
KDD CUP 99 Data
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_kddcup99
data = fetch_kddcup99()
df = pd.DataFrame(data.data)
df.drop([1,2,3], axis = 1, inplace = True)
df = df.astype(np.float32)
# df = df.select_dtypes(exclude=['object'])
y = data.target
df.dtypes
0 float32
4 float32
5 float32
6 float32
7 float32
8 float32
9 float32
10 float32
11 float32
12 float32
13 float32
14 float32
15 float32
16 float32
17 float32
18 float32
19 float32
20 float32
21 float32
22 float32
23 float32
24 float32
25 float32
26 float32
27 float32
28 float32
29 float32
30 float32
31 float32
32 float32
33 float32
34 float32
35 float32
36 float32
37 float32
38 float32
39 float32
40 float32
dtype: object
Adding noise to features to not have perfect problem
dimensions = df.shape #to get the dimesion of the data
noise = np.random.rand(dimensions[0], dimensions[1])
noisy_df = df + df * noise # to add noise the existing data
Checking the targets
pd.Series(y).value_counts()
b'smurf.' 280790
b'neptune.' 107201
b'normal.' 97278
b'back.' 2203
b'satan.' 1589
b'ipsweep.' 1247
b'portsweep.' 1040
b'warezclient.' 1020
b'teardrop.' 979
b'pod.' 264
b'nmap.' 231
b'guess_passwd.' 53
b'buffer_overflow.' 30
b'land.' 21
b'warezmaster.' 20
b'imap.' 12
b'rootkit.' 10
b'loadmodule.' 9
b'ftp_write.' 8
b'multihop.' 7
b'phf.' 4
b'perl.' 3
b'spy.' 2
dtype: int64
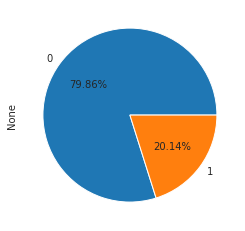
Building binary flag for ‘back’ or ‘normal’ class
yy = np.where(((y == b'back.')|(y == b'normal.')), 1, 0)
print(F"Shape: {df.shape}")
print(F"""Prevalence = {yy.sum()/len(yy)* 100:.3f}%""")
Shape: (494021, 38)
Prevalence = 20.137%
pd.Series(yy).value_counts().plot(kind ="pie", autopct="%1.2f%%")
plt.show()
noisy_df.head()
| 0 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | ... | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0 | 210.804036 | 6844.436574 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.888843 | 0.0 | ... | 12.502868 | 11.185510 | 1.111647 | 0.0 | 0.182288 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 1 | 0.0 | 240.040258 | 755.161401 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.927321 | 0.0 | ... | 31.836429 | 36.460213 | 1.217937 | 0.0 | 0.098349 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 0.0 | 359.574976 | 2614.731730 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.506819 | 0.0 | ... | 48.112809 | 30.087684 | 1.936690 | 0.0 | 0.054079 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 3 | 0.0 | 324.864701 | 2027.837786 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.845100 | 0.0 | ... | 52.215076 | 69.985597 | 1.183668 | 0.0 | 0.031935 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 4 | 0.0 | 340.145440 | 2828.912572 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.280997 | 0.0 | ... | 71.912794 | 93.026926 | 1.645168 | 0.0 | 0.034165 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
5 rows × 38 columns
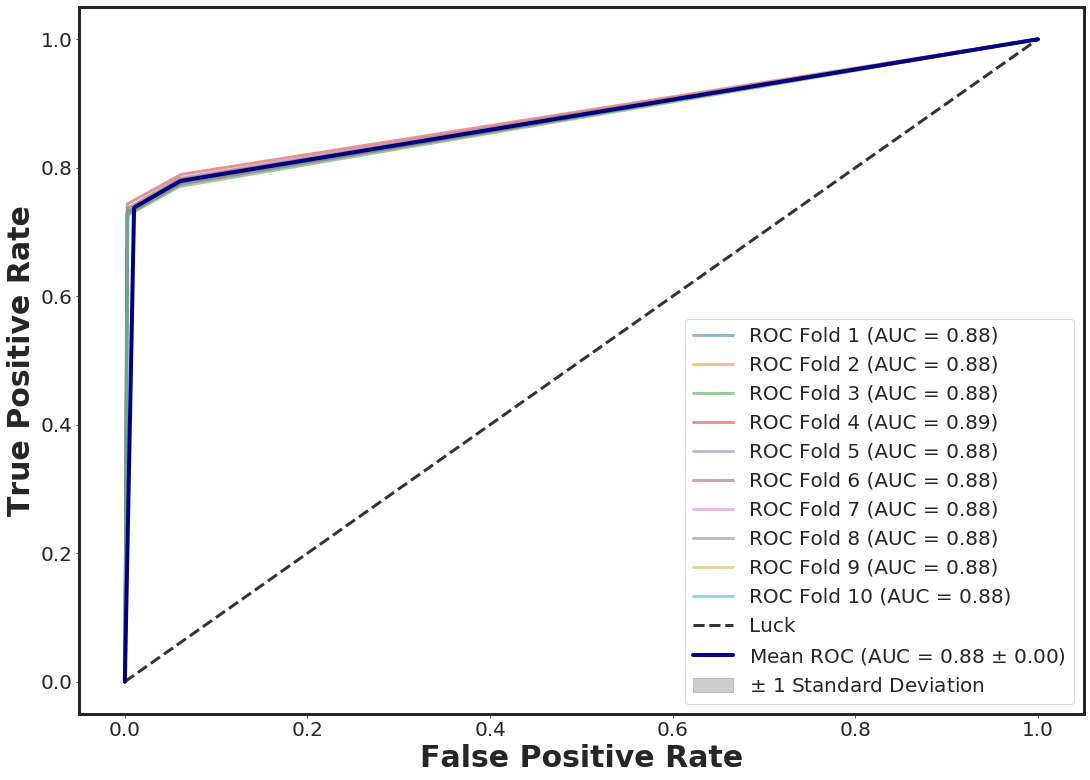
ROC Curve + 10-folds CV with XGBOOST
_plot_roc_nfolds_xgboost(noisy_df.loc[:, [ 11, 40]], yy, n_folds = 10, n_estimators = 3)
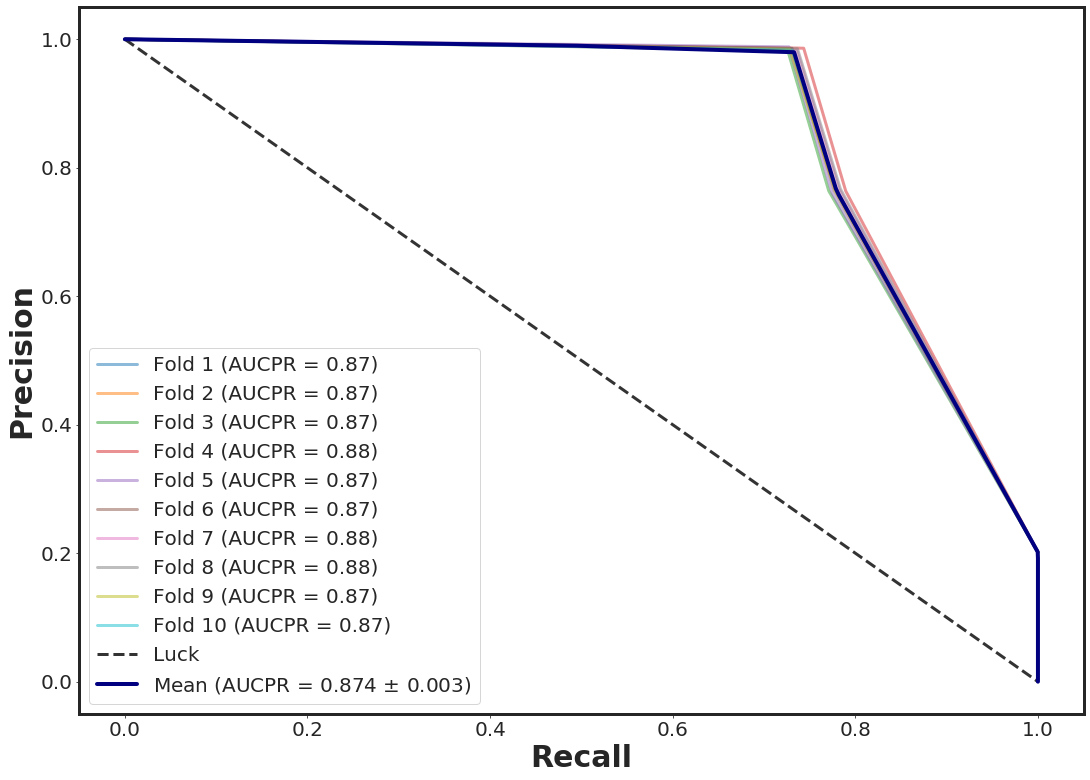
Precision Curve + 10-folds CV with XGBOOST
_plot_pr_nfolds_xgboost(noisy_df.loc[:, [11, 40]], yy, n_folds = 10, n_estimators = 3)